- Product
- Load Cell
- Force Sensor
- Torque Sensor
- Dynamometer
- Junction box
- Load cell amplifier
- Weight indicator
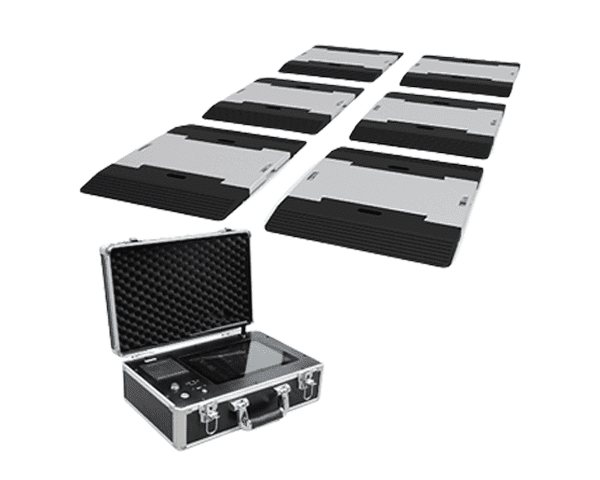
- Portable Truck Scale
- Crane scale
- Micro Load Cell Single Point Load Cell Planar beam load cell Digital Load Cell Shear Beam Load Cell Bellow beam load cell S type load cell Spoke type load cell Truck scale load cell Canister Load Cell Weigh Modules
-
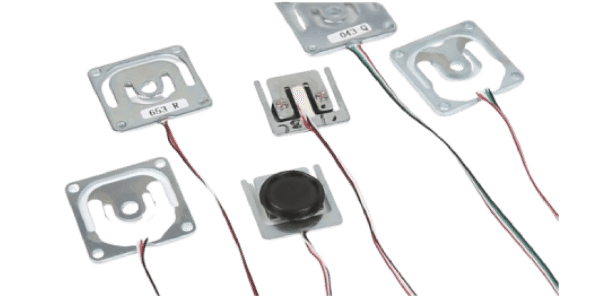
Micro Load Cell
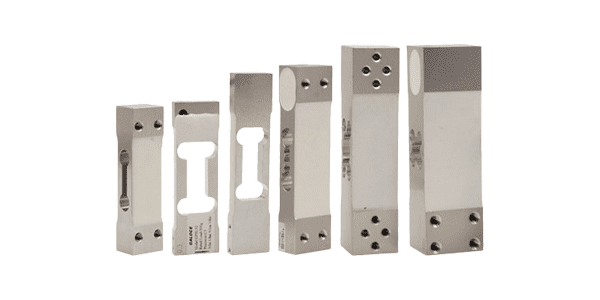
Single Point Load Cell
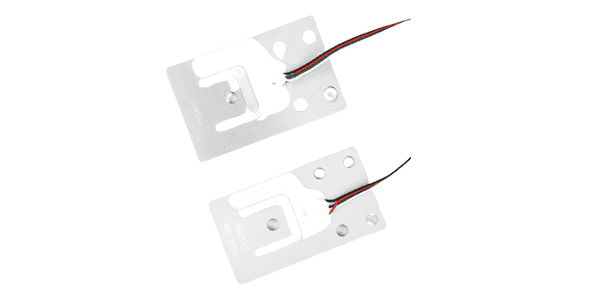
Planar beam load cell

Digital Load Cell
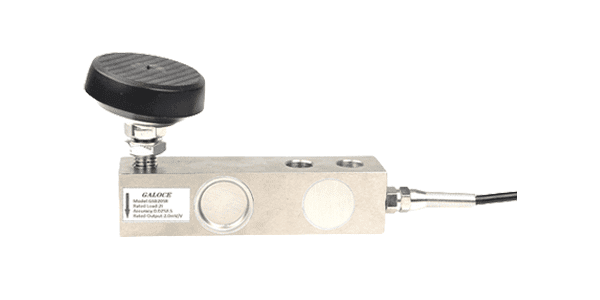
Shear Beam Load Cell
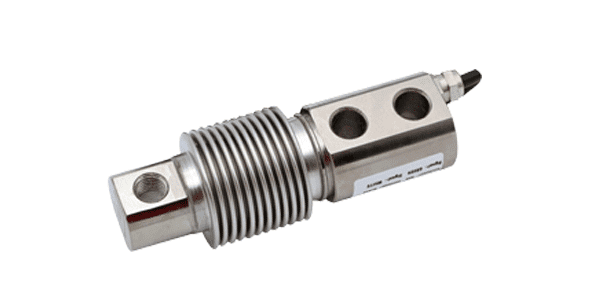
Bellow beam load cell

S type load cell

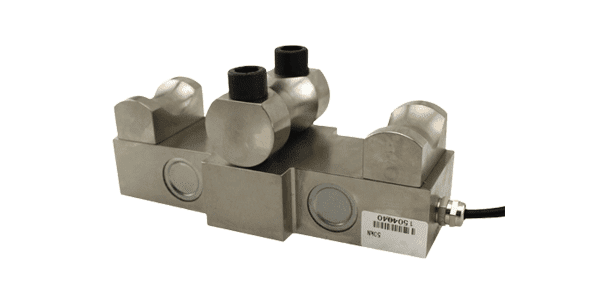
Spoke type load cell

Truck scale load cell
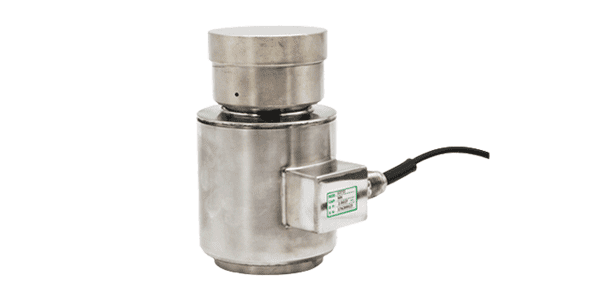
Canister Load Cell
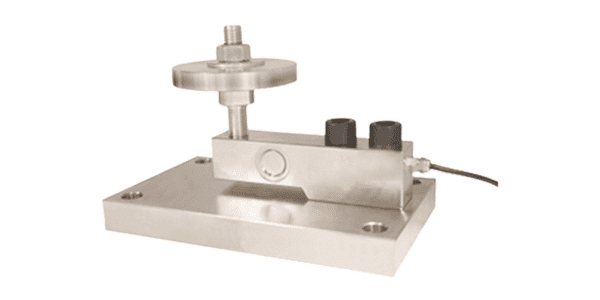
Weigh Modules
- Miniature load cell Force washers load cell Tension Compression load cell Three-axis load cell Rope tension load cell Load Pin Load Cell
-

Miniature load cell

Force washers load cell

Tension Compression load cell
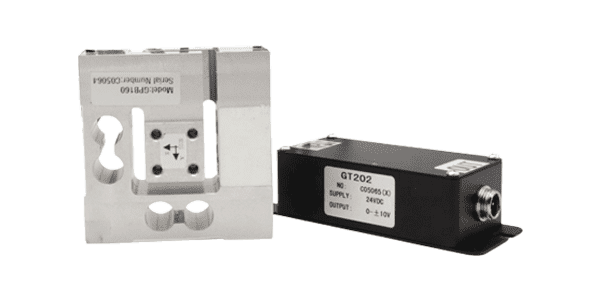
Three-axis load cell
Rope tension load cell

Load Pin Load Cell
- Stainless steel Junction box Plastic junction box Waterproof plastic junction box
-
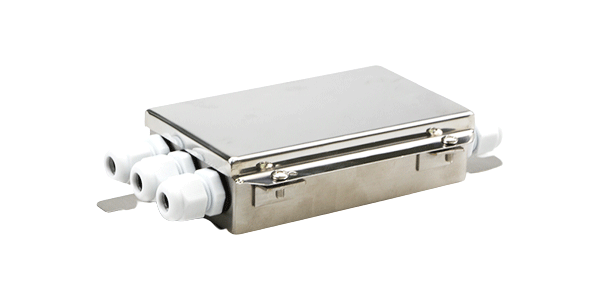
Stainless steel Junction box
Plastic junction box
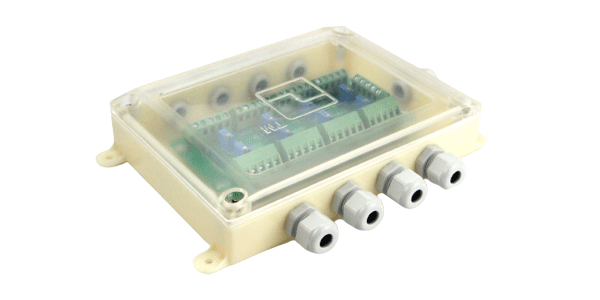
Waterproof plastic junction box
- Analog Weight transmitter Digital Weight transmitter Wireless transceiver
-

Analog Weight transmitter

Digital Weight transmitter

Wireless transceiver
- Platfrom scale indicator Truck scale indicator Belt scale indicator Weighing controller Torque meter Big screen
-

Platfrom scale indicator

Truck scale indicator

Belt scale indicator

Weighing controller

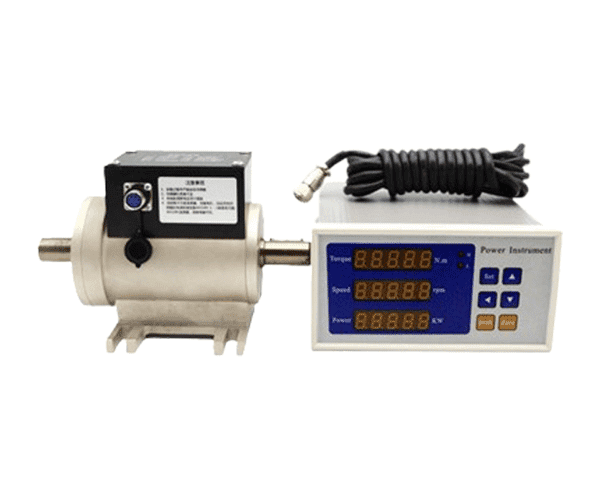
Torque meter

Big screen
- Solution
- Intelligence field Commercial scale Household Scales Transportation Medical field Agriculture machinery Construction machinery Industrial Process Control and Automation
-

Intelligence field

Commercial scale

Household Scales

Transportation

Medical field

Agriculture machinery

Construction machinery
Industrial Process Control and Automation
- Service
- Support
- IOT
- About us