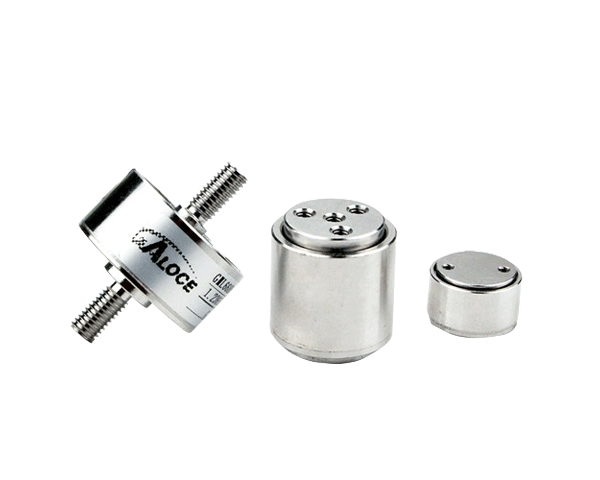
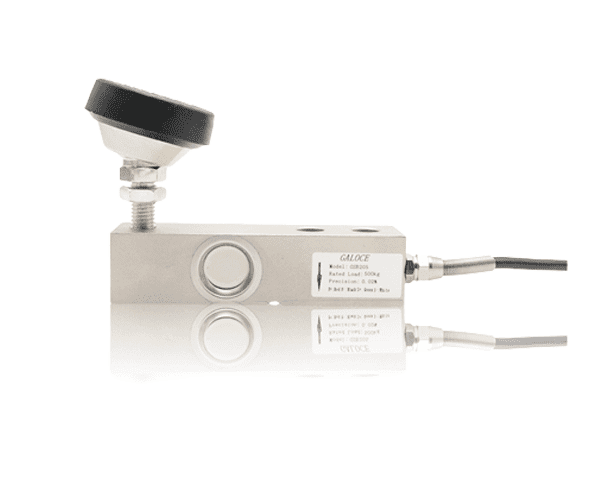
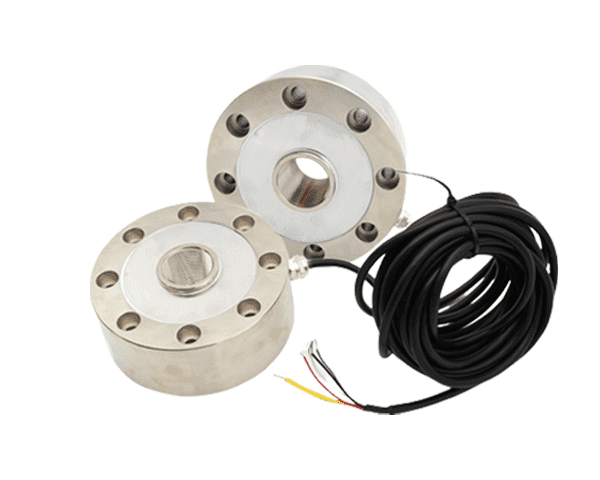
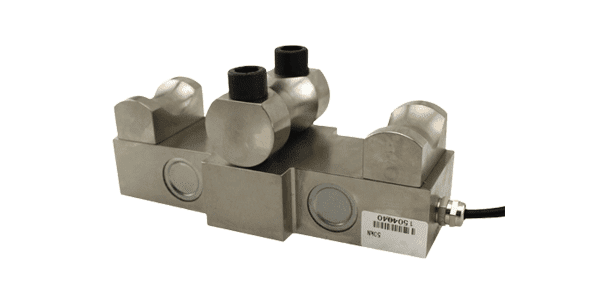
What is a load cell
A load cell is a transducer that converts force into a measurable electrical signal output.
What is the principle behind load cells?
Most load cells rely on strain gauges to measure force. Typically, four strain gauges are arranged in a Wheatstone bridge circuit, which balances the two legs of the bridge. The strain gauges are attached to a spring element—usually made of steel or aluminum—that is strong yet slightly flexible. When subjected to sufficient pressure, either compression from above or tension from below, the strain gauges deform slightly and then return to their original shape.
These gauges measure the deformation of the spring element with great precision. The directional pressure produces an electrical signal proportional to the applied force. In a typical load cell, this micro-deformation is electronically converted into an accurate weight reading, allowing precise measurement of the object's weight.
What is a strain gauge?
Strain gauges (or strain gages) are widely used sensors for measuring stress on materials under load. Established since the mid-20th century, they serve as a reliable method for monitoring material properties. Strain gauges can function as standalone transducers or be connected in series within a Wheatstone bridge to accurately measure unknown resistance and differential values. They are commonly used in load cell setups for various industrial purposes, including precision weighing and long-term monitoring of strain and material behavior.
What is the Wheatstone Bridge?
A Wheatstone bridge is a circuit made up of four resistors, known as the bridge arms. It measures changes in physical quantities by detecting variations in resistance. A microcontroller reads the voltages across the variable resistors and processes these signals to calculate the corresponding physical changes. This method provides highly accurate measurements.
Load Cell Specifications
Rated Capacity
The maximum weight or force the sensor can measure, typically expressed in Newtons (N), kilograms (kg), or pounds (lb).
Sensitivity
The ratio of output signal to applied force, usually given in mV/V (millivolts per volt).
Non-linearity
The maximum deviation between the actual output and the ideal linear output, expressed as a percentage of the rated capacity.
Hysteresis
The maximum difference in output when the load is increasing versus decreasing, indicating repeatability error.
Repeatability
The consistency of output when the same load is applied multiple times.
Zero Balance (Zero Output)
The output offset when no load is applied, typically expressed in mV/V.
Operating Temperature Range
The environmental temperature range within which the load cell can operate normally.
Compensated Temperature Range
The temperature range over which the load cell output is temperature compensated to maintain accuracy.
Temperature Effect
The influence of temperature changes on zero balance and sensitivity, usually expressed as a percentage per degree Celsius (%/°C).
Input Resistance
The resistance at the input terminals of the Wheatstone bridge inside the load cell, measured in ohms (Ω).
Output Resistance
The resistance at the output terminals of the Wheatstone bridge, measured in ohms (Ω).
Insulation Resistance
The electrical insulation resistance between the load cell elements and the case, usually measured in megaohms (MΩ).
Excitation Voltage
The recommended supply voltage range for the load cell, typically between 5V and 15V DC.
Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
The level of protection against dust and water, such as IP65, IP67, etc.
Mechanical Dimensions and Mounting
Physical size, mounting hole locations, and installation method of the load cell.
Load Cell Accuracy
Load cells sold by Phidgets Inc. are categorized into different types, as mentioned above, as well as different accuracy classes. An overview of general accuracy is available in the table below:
| Class | Total Error |
|---|---|
| C4 | 0.020% |
| C3 | 0.025% |
| C2 | 0.031% |
| C1 | 0.053% |
| Consumer | 0.1% |
As shown above, class C4 load cells have less total error, and provide greater performance regarding accuracy, repeatability, and drift.
Load Cell Output Signal
- Signal Type: Typically an analog voltage signal, weak and proportional to the applied force.
- Output Range: Typical outputs are in the millivolt (mV) class, with common full-scale outputs of a few millivolts to tens of millivolts.
- Signal Characteristics: The output signal varies linearly with load, and directional pressure produces a corresponding change in voltage.
- Sensitivity: Expressed as mV/V, it indicates the number of output millivolts corresponding to each volt of excitation voltage, e.g., 2 mV/V.
- Excitation Voltage: The output signal is dependent on the excitation voltage applied to the load element, which is usually 5V or 10V DC.
- Signal Processing: Due to the weak signals, amplifiers and filters are usually required for signal conditioning before digital conversion.
- Output Interface: The output can be analog, or it can be converted to a digital signal by a built-in or external analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
- Temperature effects: The output signal may be affected by temperature changes and requires temperature compensation.
IP Rating of Load Cell
What is an IP Rating?
An IP rating, or ingress protection rating, is a fancy way to tell how well an electrical device's enclosure will keep water and gunk from getting inside. IP ratings are commonly found on consumer products ranging from cell phones to watches to—you guessed it—industrial scales.
As defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission in the IEC 60529 standard, IP ratings consist of the letters IP and two numbers.
The first digit rates the enclosure's effectiveness at blocking intrusion from SOLID particles on a scale of 0 to 6 (with a rating of 6 offering the most protection).
The second digit rates for LIQUID protection on a scale of 0 to 8 (with a rating of 8 providing the most protection).
IP Rating Explained
To help you determine the exact level of protection provided by each IP rating, we've gone ahead and created several easy-to-use tables. Each table is organized from the smallest level of protection to full dust and water resistance.
Particle Intrusion Protection (First Digit)
| Level | Object Size Protection | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | No protection |
| 1 | > 50 mm | Hands or tools |
| 2 | > 12.5 mm | Small tools or fingers |
| 3 | > 2.5 mm | Fasteners, wire, etc |
| 4 | > 1 mm | Dirt and debris |
| 5 | Some Dust | No dust deposits that would effect use |
| 6 | Dust Proof | No intrusion of dust into enclosure |
Liquid Intrusion Protection (Second Digit)
| Level | Water Droplet Protection | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | No protection |
| 1 | Dripping | Vertical falling drops of water |
| 2 | Drips tilted at 15° | Dripping water when device tilted up to 15° from normal position |
| 3 | Spraying | Water spray up to 60° from vertical |
| 4 | Splashing | Water splashed on enclosure from any angle |
| 5 | Water Jets | Water pressurized through 6.3 mm nozzle from any angle |
| 6 | High Power Water Jets | Water pressurized through 12.5 mm nozzle from any angle |
| 7 | Immersion up to 1 Meter | Submerged up to 1 meter for 30 minutes |
| 8 | Immersion over 1 Meter | Submerged depth and time set by manufacturer |
Load Cell Material
Structurally, a load cell has a metal body to which strain gauges have been secured. The body is usually made of aluminum, alloy steel, or stainless steel which makes it very sturdy but also minimally elastic. This elasticity gives rise to the term "spring element", referring to the body of the load cell.
Types of Load Cell
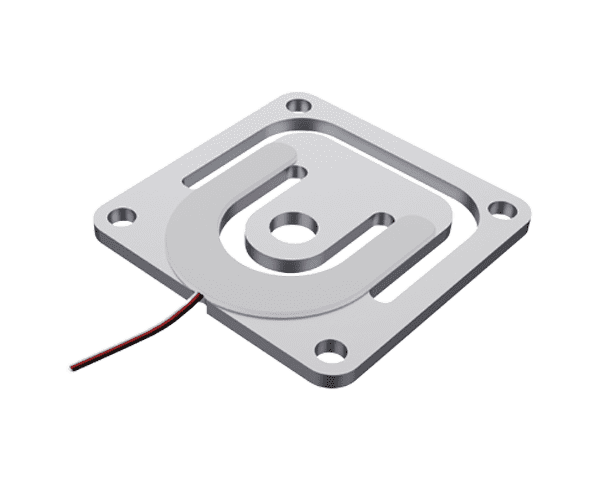
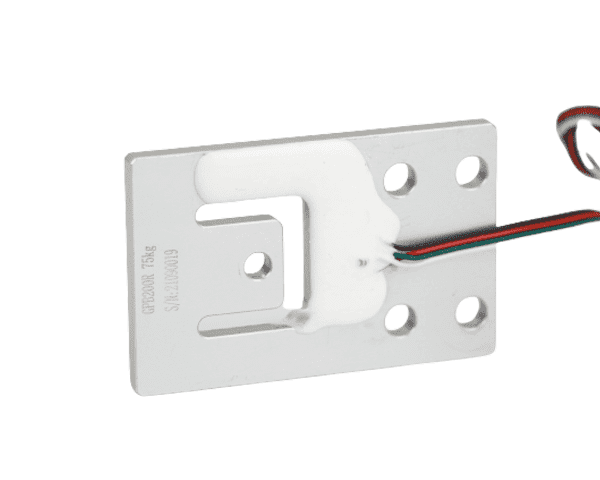
Micro Load Cells
- Definition: Micro Load Cell is a small-sized sensor that is used to measure force or weight. They typically utilize high-precision strain gauge technology in compact designs for space-constrained environments, providing accurate force or weight measurements in confined spaces and high sensitivity for precision measurement needs.
- Application: It is designed to provide accurate and precise measurements in various applications.Force feedback measurements in medical devices such as syringes and surgical instruments; microelectronics manufacturing such as chip assembly, precise weighing and force detection of micro-components; robotics such as force sensing for robotic grippers to improve operational accuracy; laboratory instruments such as weighing of trace samples and mechanical testing of materials; aerospace such as precise load monitoring of tiny components; consumer electronics such as pressure sensing of touchscreens, and force detection in wearable devices. force detection in wearable devices, etc.
- Installation: Mounting, usually by screwing or adhesive bonding, ensures that the sensor is in close contact with the object to be measured. Pre-stressing during mounting needs to be avoided to avoid compromising measurement accuracy. Mounting directly near the point where the force is applied ensures accuracy of measurement and speed of response.
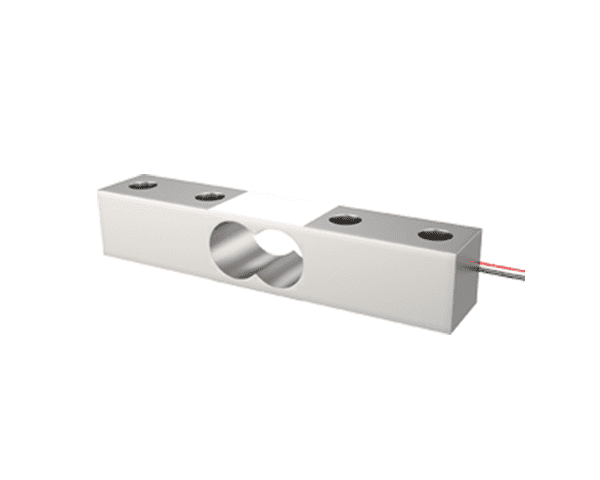
Single Point Load Cells
- Definition: A Single Point Load Cell is a type of sensor that is used to measure the weight or force applied to it at a single point.
- Application: It is commonly used in weighing scales, industrial equipment, and other applications where accurate weight measurement is required.
- Installation: Single-point load cells typically have an arrow showing which direction the load should be applied. One end of the load cell is secured to the base of the platform, while the other is secured to the top plate. These load cells cannot be combined to increase weighing capacity.
Planar Beam Load Cells
- Definition: The planar beam load cell is a type of load cell that is designed to measure the force or weight applied to it. It consists of a flat, rectangular beam made of a high-quality alloy material.
- Application: The beam is typically mounted on a base or platform, and the force or weight is applied to the top surface of the beam.
- Installation: Our planar beam load cells (matched set of 4) have four mounting holes for easy connection onto a frame, and a single mounting hole that is often used with a rubber pad or vibration mount that rests on the ground.
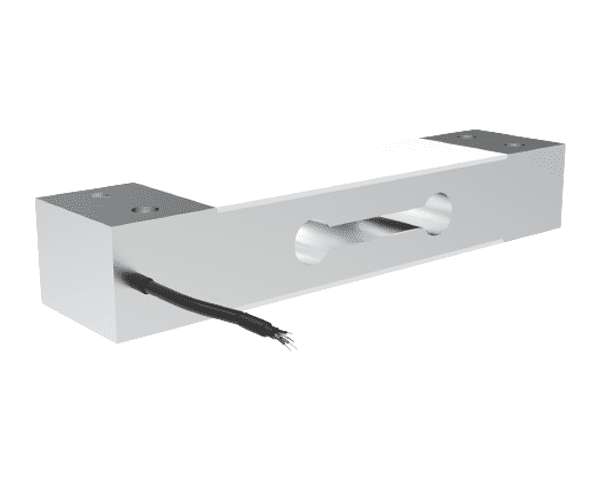
Shear Beam Load Cells
- Definition: A shear beam load cell is a type of load cell that is commonly used in weighing applications.
- Application: It is designed to measure the force or weight applied perpendicular to its axis.
- Installation: Usually installed horizontally on the weighing platform or support structure at the point of force, need to be fixed firmly, usually with the mounting bracket, adjusting bolts, to ensure that the load cell force uniformity.
Spoke Type Load Cells
- Definition: A spoke type load cell is a type of load cell that is designed to measure the force or weight applied to it. It consists of a central hub with multiple spokes radiating outwards. When a force is applied to the load cell, the spokes deform, and this deformation is measured to determine the applied force.
- Application: Core weighing components for weighbridges, vehicle scales, railroad scales; weighing systems for large silos and hoppers; load monitoring for cranes and hoists; mechanical testing of heavy machinery and equipment
- Installation: Usually installed at the pivot point of the weighing platform or support structure, it is necessary to ensure that the load direction of the load cell is the same as the actual direction of force.
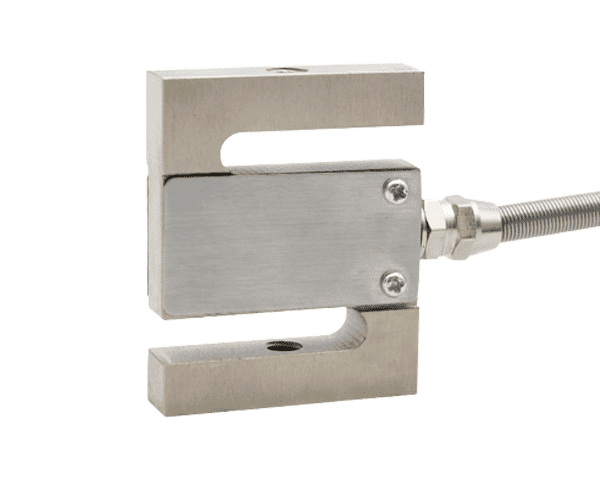
S type Load Cells
- Definition: S type load cells receive tension or compression output readings. It provide superior performance in an compact, versatile package.
- Application: They are are widely used in small hopper and tank weighing systems, hybrid systems with lever work, belt weighers and other load carriers with multiple load cells.
- Installation: S-type load cells are generally used with eye bolts or rod end bearings which provide an easy connection point to the rest of a system.
Digital Load Cells
- Definition: A digital load cell is a type of sensor that is used to measure the weight or force applied to it. It converts the mechanical force into an electrical signal that can be easily read and interpreted by a digital display or computer system.
- Application: Because of its built-in digital module, the output is digital signal, so it is mainly used in intelligent shelves, intelligent gravity cabinets, garbage collection and other occasions.
- Installation: The installation of digital load cell is similar to the traditional analog Load Cell, need to ensure that the sensor force in the right direction; need to connect the appropriate digital interface and power supply lines; attention to protection measures to avoid moisture or damage to the digital circuitry.
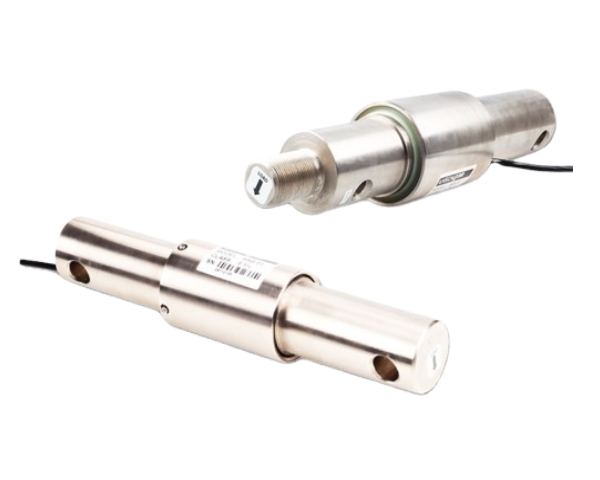
Canister Load Cells
- Definition: The Canister Load Cell is a type of load cell that is designed to measure and monitor the weight or force applied to it. It consists of a cylindrical shape with threaded holes on each end for easy installation.
- Application: It is the weighing core component of weighbridge, car scale, railroad scale, as well as the weighing of large silos, tanks, hoppers and other containers.
- Installation: Usually installed at the pivot point of the weighing platform or support structure, it is necessary to ensure that the axial load direction of the load cell is the same as the actual direction of force.
What are Load Cells Used for
Load Cells in Agriculture
1. Plantation industry
- UAV applying fertilizer, spraying, watering: Monitoring of irrigation water/feed usage and control of irrigation/sprinkler system on and off through tank weight changes
- Weighing produce: Load cell can be used to measure the weight of crops, such as fruits, vegetables, or grains. This can be useful for determining harvest yields, as well as for determining the appropriate amount of fertilizers or pesticides to use.
- Weighing fertilizer: Load cells - frequently shear beams and weigh bar - are commonly found underneath fertilizer carts and manure spreaders to ensure proper distribution.
2. Livestock raising
- Livestock Scale: Load cells can be used to accurately measure the weight of livestock, such as cows, pigs, or sheep. This can be helpful for monitoring the health and growth of the animals, as well as for tracking production and yield.
- Weighing feed: Load cells can be used to measure the weight of feed for livestock, such as hay, grain, or feed mix. This can be helpful for tracking feed usage and for optimizing the nutritional needs of the animals.
- Milk yield monitoring system for cows: Real-time monitoring of milk production from cows helps farmers understand milk yield and quality. Combined with automatic milking equipment, it realizes automatic data collection and management.
Load Cells in Commercial
1. Retail industry
- Electronic weighing equipment: electronic cash register scales, pricing scales, platform scales, floor scales. Application Scenarios: Used in supermarkets and vegetable markets for weighing and pricing bulk commodities such as vegetables, fruits and meat; In logistics and warehousing, it is used for weighing goods to ensure the accurate weight of shipment; Weighing of parcels in the courier industry to calculate freight charges.
- Vending machine: vending machine for drinks and snacks. Application Scenario: Detect whether the goods are taken out through load cell to realize intelligent inventory management; Measuring the weight of goods, judging the remaining amount of goods, and automatic replenishment reminder.
- Shelf Monitoring System: Intelligent Shelf Weighing Sensor. Application Scenario: Installing load cell on the shelves of shopping malls or convenience stores for real-time monitoring of product inventory; Combine with IOT technology to realize automatic replenishment and sales data analysis.
2. Household industry
- Intelligent Furniture: Smart Mattress, Smart Sofa, Intelligent Trash Can, Smart Litter Pan. Application Scenario: Mattress with built-in load cell monitors human body weight and sleeping posture to provide healthy sleep data; The sofa has a built-in load cell to detect sitting posture and recognize users; Monitor the weight of garbage to help users reasonably arrange garbage sorting and cleaning time.Combined with the smart home system, it realizes garbage volume statistics and reminders; The weighing sensor records the weight change of the cat when using the litter box in real time, combines with the algorithm to distinguish the weight of excreta and litter, and accurately counts the amount of excreta on a single occasion, providing data support for health monitoring.
- Electronic weighing equipment: Kitchen Scale, Ingredient Weigher, Body Scale. Application Scenario: Accurate weighing of ingredients in the home kitchen helps to control the amount of ingredients and nutritional intake; Accurate baking ingredients to ensure the quality of food.
Load Cells in Industry
1. Building Industry
- Weighing System for Concrete Batching Plant: Product Type: Shear Beam Load Cell. Application Scenario: It is used for accurate weighing of aggregates, cement and additives in the hopper of the mixing plant to ensure the accurate proportioning and guarantee the quality of concrete; Monitor the weight of raw materials in real time and control the feeding process automatically.
- Crane Load Monitoring: Product Type: Spoke Load Cell, Tension Load Cell. Application Scenario: Installed on crane hook or sling, real-time monitoring of lifting weight to prevent overloading and ensure construction safety; Monitor the dynamic load changes during the lifting process.
- Structural Stress and Load Testing: Product Type: High Precision Strain Load Cell. Application Scenario: Used for stress testing and load monitoring of bridges and building structures to assess structural safety; Stress monitoring of key structural components during construction.
2. Manufacturing industry
- Weighing Control for Automated Packaging Equipment: Product Type: Digital Load Cell, Shear Beam Load Cell. Application Scenario: Weighing of products on the packaging line ensures that package weights are in compliance with standards and prevents missing or overweight; Automatic metering and dispensing control to improve production efficiency and product consistency.
- Material Dosing System for Production Line: Product Type: Shear Beam Load Cell, Digital Load Cell. Application Scenario: Accurate weighing of raw materials and automatic dosing to ensure accurate product formulation; The dosage process control in chemical, food, pharmaceutical and other industries.
- Mechanical Equipment Load Monitoring: Product Type: Spoke Load Cell, Tension Load Cell. Application Scenario: Monitor the load of mechanical equipment at work to prevent overload damage; Equipment maintenance and failure warning.
- Quality Inspection and Mechanical Testing: Product Type: High-precision Digital Load Cell. Application Scenario: Mechanical property testing of materials such as tensile, compression and bending; Quality inspection and certification of products before shipment.
Load Cells in Medical Industry
- Medical Bed Weighing System: Product Type: Small Shear Beam Load Cell, Digital Load Cell. Application Scenario: Integrated in smart beds, real-time monitoring of patients' weight changes, assisting doctors in assessing patients' health status; Monitoring patient's weight is used for drug dosage adjustment and nutrition management.
- Load Monitoring for Medical Equipment: Product Type: Spoke Load Cell, Small Tension Load Cell. Application Scenario: Load monitoring of internal components of medical imaging equipment (e.g., MRI, CT scanner) to ensure safe operation of the equipment; Force feedback control of surgical robotic arms and auxiliary equipment to improve operation precision and safety.
- Rehabilitation Training Equipment: Product Type: High-precision Digital Load Cell, Compression Load Cell. Application Scenario: Used in strength training and rehabilitation equipment to measure the force exerted by the patient and monitor the progress of rehabilitation; Provide real-time feedback to help patients adjust the training intensity.
- Medical Weighing Devices: Product Type: High Precision Platform Load Cell, Digital Load Cell. Application Scenario: Hospital weight scales and baby scales to provide accurate weight data; Weighing of medicines and precise measurement in the dispensing system.
- Drug R&D and Testing: Product Type: Miniature High Precision Load Cell. Application Scenario: Micro-weighing of drug samples in the laboratory to ensure accurate formulation; Mechanical properties testing to assess compression strength and stability of drug tablets.
How to Test a Load Cell?
Load cells convert mechanical forces into precise electrical signals for accurate weight measurement in a variety of applications. The reliability of the load cell is very important and the slightest deviation can have consequences. Regular testing of load cells will maintain their accuracy and reliability over time.Knowing how to test load cells can improve operational efficiency and avoid costly errors and equipment failures.
Things you need to know before testing
Before testing load cells, it is important to understand the various types and configurations available. Load cells are generally categorized into compression, tension, and shear beam types, each designed for a specific application. Compression load cells measure the force applied along their axial direction, while tension load cells measure the force applied in the direction of stretch. Shear beam load cells are versatile and commonly used in platform scales.
Familiarize yourself with the basic components of a load cell, including the strain gauge that detects deformation and generates an electrical signal, and the signal conditioning circuitry that amplifies and converts the signal for an accurate reading. Understanding how these components interact will help you accurately interpret test results.
Additionally, knowing the load cell's rated capacity and environmental conditions will ensure that you conduct your tests safely and efficiently, maintaining the integrity of your measurements.
Tools and Equipment Required
To test a load cell, you will need the following tools and equipment:
- Multimeter: For measuring voltage and resistance.
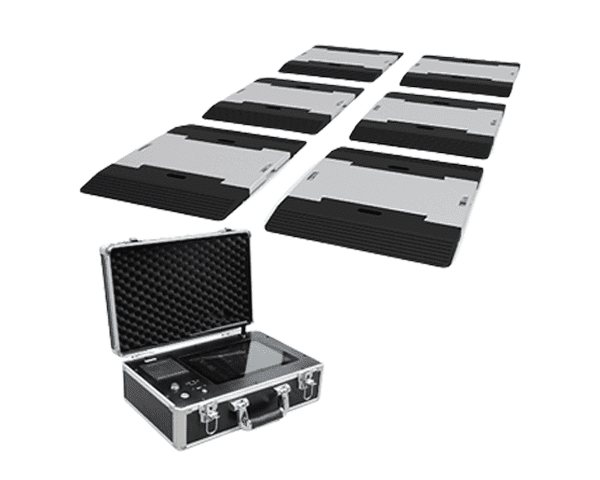
- Test Weights: To apply known loads for calibration.
- Load Cell Simulator: To emulate load conditions without physical weights.
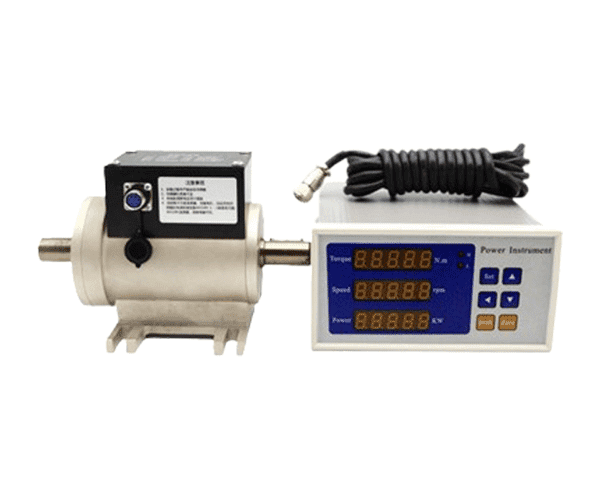
- Load Cell Tester: A specialized device that provides accurate readings and diagnostics.
Steps to Test a Load Cell
Testing a load cell requires several steps to ensure accuracy. Here is a detailed guide on how to check a load cell:
- Visual Inspection: Start with a careful visual examination. Look for any physical damage such as cracks, dents, or corrosion that could impair performance. Verify that all electrical connections are secure and show no signs of wear or fraying.
- Zero Balance Test: Next, conduct a zero balance test. This means confirming that the load cell reads zero when no load is applied. To perform this, disconnect the load cell from any weight and measure its output signal. The reading should be close to zero, typically within ±1% of the full-scale output. Any significant deviation may indicate calibration problems or potential damage to the load cell.
- Resistance Checks: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the load cell's wiring. Compare these measurements against the manufacturer's specifications—for strain gauge load cells, typical resistance values are around 350Ω or 700Ω. A variation greater than ±5% from these values could suggest internal damage or wiring faults.
- Load Application Test: Apply known test weights gradually to the load cell and record the output readings at each step. The output should increase linearly with the applied load, confirming that the load cell is functioning correctly.
- Simulator Testing: If using physical weights is impractical, a load cell simulator can be employed. Connect the simulator to the load cell and set it to various weight values to check whether the output matches the expected readings. This method is especially helpful for troubleshooting without needing actual weights. It's important to note that while a load cell simulator effectively emulates expected electrical outputs for troubleshooting the weighing system, it does not evaluate physical damage or mechanical issues within the load cell itself.
-
Troubleshooting Common Issues: If you experience problems such as signal fluctuations or drift, try the following steps: Ensure all wiring is secure and free from corrosion.
- Recalibrate the load cell according to the manufacturer's instructions if the readings are inconsistent.
- Consider environmental factors like temperature changes or vibrations that could impact performance.
Understanding the Results
When testing a load cell, normal results show that the output corresponds closely to the expected values based on the applied load. For example, a load cell with a rated sensitivity of 2 mV/V, when powered by a 10V excitation voltage, should produce an output of about 20 mV at its full rated capacity. Additionally, consistent readings across multiple tests are a strong indication of proper functioning.
Abnormal results may appear as unstable or fluctuating outputs, failure of the reading to return to zero once the load is removed, or significant discrepancies from the expected output values. For instance, if the zero balance variation exceeds the tolerance specified in the datasheet—typically around 1%—this could indicate damage caused by overloading or internal defects.
Fluctuations in the signal may be caused by electrical interference or poor wiring connections. If the readings show drift over time, it is advisable to recalibrate the load cell and investigate any environmental factors that might be affecting its performance.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional assistance is essential to preserving the accuracy and reliability of your load cell systems. The following are important indicators that expert service may be required:
- Ongoing or unresolved problems
- Requirements for calibration and certification
- Visible physical damage
At GALOCE, we specialize in solving complex load cell problems and providing viable weighing solutions. Our team is able to provide comprehensive services and customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.
For more guidance and support, contact GALOCE today!